Introduction
Gut health is a topic that has gained significant attention in recent years, with mounting evidence linking the condition of our gut to various aspects of our overall health and well-being. One dietary approach that has gained popularity for its potential benefits on gut health is the ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet.
This article digs into the influence of keto diet on gut health
Definition of the Keto Diet
The ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat eating plan that forces the body to enter a state of ketosis. In this state, the body primarily relies on ketones, which are produced from fat breakdown, as its main source of energy instead of glucose derived from carbohydrates. The typical macronutrient composition of a keto diet consists of approximately 70-75% fat, 20-25% protein, and only 5-10% carbohydrates.
By severely limiting carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the primary goal of this dietary approach is to shift the body’s metabolism from relying on glucose for energy to utilizing stored fats instead. This metabolic adaptation leads to increased production and utilization of ketones by various tissues in the body.
Importance of Gut Health
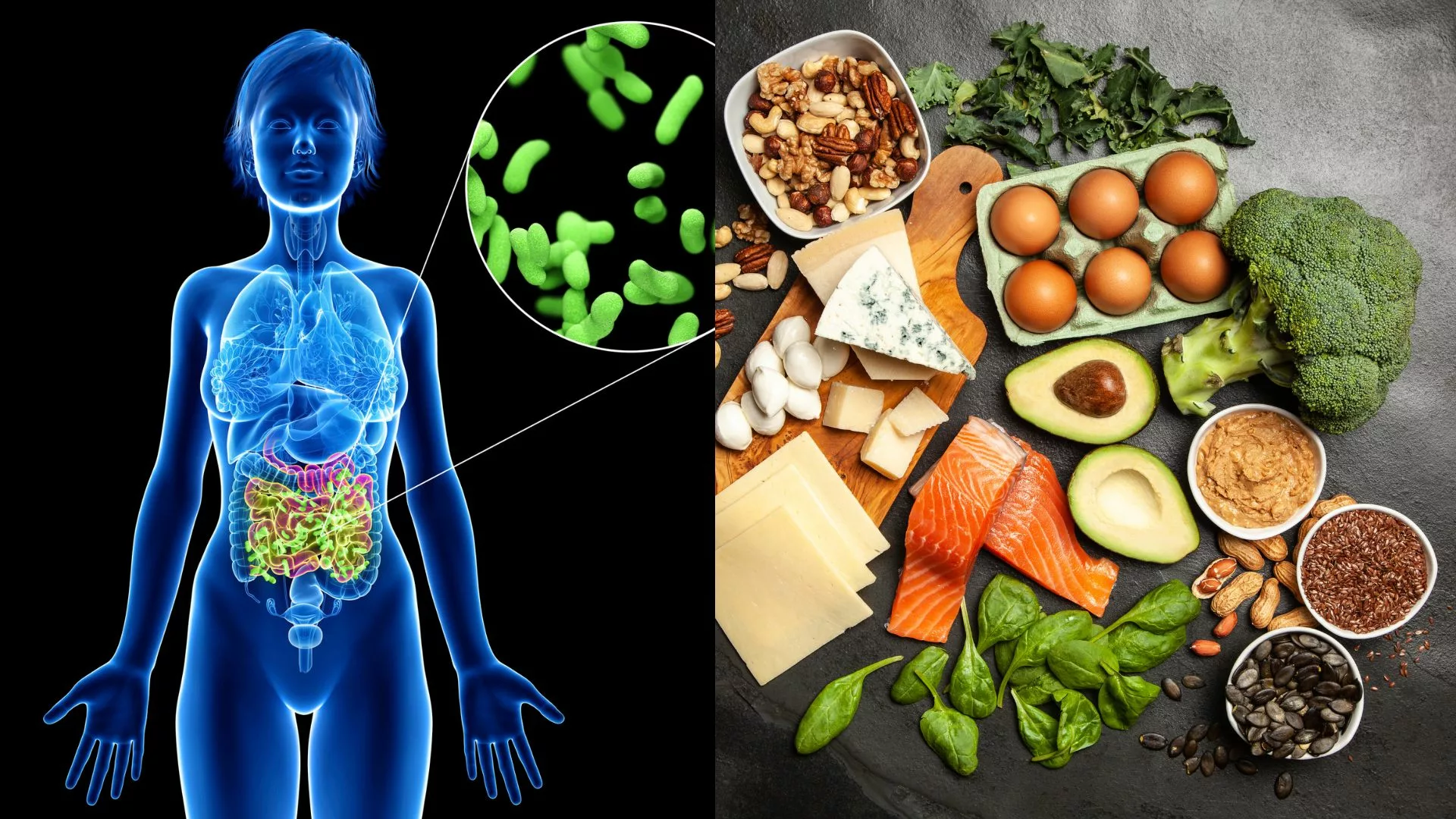
The gut plays a crucial role in our overall health; it not only serves as a site for digestion and absorption but also houses trillions of microorganisms collectively known as the gut microbiota or microbiome. These microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, fungi, archaea, and other microbes that coexist with us symbiotically. The gut microbiome has a complex relationship with human physiology and contributes significantly to various processes such as nutrient metabolism, immune system function modulation, vitamin synthesis (e.g., B vitamins), protection against pathogens through competition for resources, and niche occupation within the gut ecosystem.
Beyond these vital functions though, recent research suggests that the gut microbiota may also be involved in influencing other aspects of our health, including mental health, metabolism, and immune system regulation. Dysbiosis, an imbalance or disruption of the gut microbiota, has been associated with a range of conditions such as obesity, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), allergies, and even neurological disorders like anxiety and depression.
Given the intricate relationship between our gut and overall well-being, exploring the impact of dietary interventions like the ketogenic diet on gut health becomes crucial. This article aims to delve into the influence of the keto diet on various aspects of gut health, such as changes in gut microbiota composition, gut barrier function, and its effects on communication within the gut-brain axis.
Overview of Gut Health
Gut health is a fundamental aspect of overall well-being, playing a pivotal role in various bodily functions. At the core of this intricate system lies the gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem consisting of trillions of microorganisms inhabiting our gastrointestinal tract. These microscopic inhabitants, primarily bacteria but also viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms, collectively contribute to maintaining homeostasis within our bodies.
Role of the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome serves several crucial functions that extend far beyond digestion. It aids in nutrient absorption, synthesizes essential vitamins and minerals, plays a vital role in modulating the immune system response, and even influences our brain health through gut-brain axis communication.
Composition and Diversity of Gut Bacteria
The composition of gut bacteria varies from person to person due to factors such as genetics, diet, lifestyle habits, and environmental exposures. The two dominant phyla found in the human gut are Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes; however, there are many other less abundant phyla present as well. Firmicutes bacteria are known for their ability to ferment carbohydrates and produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like acetate, propionate, and butyrate.
On the other hand, Bacteroidetes are involved in breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler molecules that can be absorbed by our body. The diversity within the gut microbiome is also crucial for maintaining optimal health.
A diverse microbial community indicates resilience against pathogens and better metabolic efficiency. Conversely, low microbial diversity has been associated with certain health conditions like obesity and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Impact on Overall Health and Well-being
The influence of the gut microbiome extends beyond digestion; it actively interacts with our immune system, influencing its development, function, and response to pathogens. A healthy gut microbiome helps regulate immune responses, preventing unnecessary inflammation or overreactions that can lead to autoimmune diseases. Moreover, the gut microbiome is involved in the production and regulation of various neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
Serotonin, often referred to as the “happy hormone,” influences mood stability and is largely produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, disruptions in gut microbial composition can potentially impact mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
Understanding the importance of gut health and appreciating its role in maintaining overall well-being is becoming increasingly crucial. The intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and various aspects of our health highlights the need for further research into strategies that promote a diverse and balanced microbial community within our gastrointestinal tract.
The Keto Diet: A Brief Overview
Explanation of the ketogenic diet
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate, and moderate-protein approach to eating. It was initially developed in the 1920s as a therapeutic intervention for individuals with epilepsy. However, in recent years, it has gained significant popularity as a weight loss strategy and for its potential health benefits beyond epilepsy management.
The key principle of the ketogenic diet revolves around achieving a state of ketosis. Ketosis is a metabolic state where the body primarily relies on fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates.
By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the body must adapt its energy source from glucose derived from carbohydrates to ketones produced by breaking down fats. This shift leads to numerous physiological changes within the body.
High fat, low carbohydrate, moderate protein approach
One of the distinguishing features of the ketogenic diet is its emphasis on high-fat foods while significantly restricting carbohydrates. Typically, 70-80% of daily calorie intake comes from fats sources such as avocados, nuts and seeds, olive oil, coconut oil, and fatty fish like salmon or sardines.
Carbohydrate intake is dramatically reduced to around 5-10% of total calories consumed per day. This means limiting or eliminating foods rich in carbohydrates such as grains (rice, wheat), starchy vegetables (potatoes), fruits (bananas), and sugars (table sugar).
Instead, non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens are encouraged due to their lower carbohydrate content. To prevent excessive breakdown of muscle tissue during ketosis induction or maintenance phase while maintaining satiety levels and providing essential nutrients for bodily functions such as hormone production and tissue repair/modification processes generally requires a moderate amount of protein consumption—typically around 15-20% of total calorie intake.
How it induces ketosis and shifts metabolism
When carbohydrates are restricted, the body’s primary energy source, glucose, becomes scarce. Consequently, insulin levels decrease as insulin is primarily released to regulate glucose levels in the bloodstream.
With low insulin levels, fatty acids from dietary fat or stored body fat are released and transported to the liver for conversion into ketone bodies—a process known as ketogenesis. These newly formed ketone bodies—including acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate-circulate in the bloodstream and serve as an alternative fuel source for cells throughout the body.
The brain also adapts to utilizing these ketones instead of glucose for energy. This metabolic shift has several notable effects on the body.
Firstly, it promotes efficient utilization of stored fats for energy production, contributing to weight loss and reduction in body fat percentage. Secondly, it can result in improved blood sugar control by reducing dependence on glucose-containing foods.
Some studies suggest that ketosis may have neuroprotective effects and potentially benefit individuals with neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding the basics of the ketogenic diet provides insight into its potential influence on gut health.
By significantly restricting carbohydrates while increasing fat consumption and moderating protein intake, this dietary approach triggers a metabolic state called ketosis where fatty acids are converted into ketones serving as an alternative energy source. Beyond weight loss benefits or epilepsy management goals associated with this approach lies a complex interplay between diet-induced metabolic changes and various physiological systems within our bodies including gut health.
Changes in Gut Microbiota Composition
another remarkable influence of keto diet on gut health is its effect on the composition of gut microbiota. Research has shown that this low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet leads to a reduction in certain bacteria species, most notably Firmicutes. Firmicutes are commonly associated with obesity and metabolic disorders.
Their abundance has been implicated in increased energy extraction from food, leading to weight gain and insulin resistance. Conversely, the keto diet promotes an increase in beneficial bacteria such as Bacteroidetes.
These microbes are known for their ability to break down complex carbohydrates and produce essential vitamins and nutrients. Their presence is associated with improved metabolic health and a reduced risk of chronic diseases like obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Influence on Gut Barrier Function and Integrity
The gut barrier plays a crucial role in maintaining overall gut health. It acts as a protective barrier against harmful substances while allowing nutrients to be absorbed efficiently.
The keto diet has been found to influence gut barrier function positively. One way the keto diet enhances gut barrier integrity is through enhanced production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
SCFAs are produced by certain bacteria during the fermentation of dietary fiber in the colon. They play a pivotal role in maintaining the health of intestinal cells, promoting their growth, and preventing inflammation.
In addition to SCFA production, the ketogenic diet may potentially reduce intestinal permeability. Intestinal permeability refers to how easily substances can pass through the intestinal lining into the bloodstream.
A healthy gut should have a tight junction between cells that prevents larger molecules from crossing over undesirably. Preliminary studies suggest that ketone bodies produced during ketosis may help maintain these tight junctions, reducing unwanted leakage from the intestines.
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Bidirectional Communication Line
The influence of keto diet on gut health extends beyond the gut itself. The gut and brain are intricately connected through a communication pathway known as the gut-brain axis.
Notably, the keto diet can impact this bidirectional interaction, potentially influencing mood and mental well-being. One mechanism through which the keto diet affects mood is by influencing neurotransmitter production.
The increased production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter with inhibitory effects, may contribute to a reduction in anxiety symptoms. GABA promotes relaxation and calmness by counteracting the excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain.
Moreover, as serotonin is predominantly produced in the gut, changes in gut microbiota composition brought about by the keto diet may also impact serotonin levels. Serotonin plays a vital role in regulating mood stability and has been implicated in conditions such as depression and anxiety.
Implications for Gut Health
The influence of keto diet on gut health has significant implications for overall well-being. By favorably altering gut microbiota composition, promoting beneficial bacteria, and enhancing intestinal barrier function, this dietary approach offers potential benefits beyond weight loss or metabolic improvements alone.
Furthermore, considering that imbalances in gut microbiota have been linked to various chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and even neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, understanding how dietary interventions like the keto diet influence these microbial populations could open new avenues for therapeutic interventions. However, it is important to note that individual responses to dietary changes may vary.
While some individuals may experience substantial benefits from adopting a ketogenic approach for their gut health, others might not respond as favorably or could even experience adverse effects due to underlying physiological differences or pre-existing conditions. Consulting with a healthcare professional before embarking on any significant dietary changes is always advised.
Effects on Gut-Brain Axis Communication
Impact on Neurotransmitter Production
The intricate connection between the gut and the brain, known as the gut-brain axis, plays a vital role in regulating mood and behavior. The keto diet has been shown to have a direct impact on neurotransmitter production, which further influences our mental well-being. One neurotransmitter affected by the ketogenic diet is gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps calm and relax the brain, reducing anxiety and promoting feelings of tranquility. Studies have indicated that adherence to a ketogenic diet can lead to increased GABA production in the brain, providing individuals with a natural remedy for alleviating anxiety.
Increased GABA Production Leading to Reduced Anxiety
Anxiety disorders affect millions of people worldwide, often causing significant distress and impairment in daily life. The ketogenic diet shows promise as a potential intervention for anxiety due to its ability to increase GABA production. GABA works as a calming agent within the central nervous system, helping suppress excessive neuronal activity associated with anxiety symptoms.
By enhancing GABA levels through nutritional means rather than pharmaceutical interventions, individuals may experience reduced anxious thoughts and physical manifestations of anxiety such as rapid heartbeat or restlessness. This natural approach allows those struggling with anxiety to manage their symptoms without relying solely on medication or therapy.
Potential Modulation of Serotonin Levels Affecting Mood Stability
Serotonin is another crucial neurotransmitter involved in regulating mood stability. Imbalances in serotonin levels are associated with conditions like depression and mood disorders. Interestingly, studies have suggested that adhering to a ketogenic diet may influence serotonin levels positively.
The keto diet’s high-fat content stimulates an increase in tryptophan availability—an amino acid necessary for serotonin synthesis—helping maintain adequate serotonin levels in the brain. This modulation of serotonin production may contribute to improved mood stability, reduced depressive symptoms, and an overall sense of well-being.
Unraveling the Complexities of the Gut-Brain Axis
While the effects of the keto diet on neurotransmitter production and the gut-brain axis are fascinating, it is essential to recognize that this field of research is still in its early stages. The intricate mechanisms by which gut health influences brain function are complex and multifaceted.
Researchers continue to explore how dietary interventions like the ketogenic diet can influence neurotransmitters, mood, and mental health. Further investigations are needed to uncover the full extent of these effects and determine if they can be harnessed as therapeutic strategies for individuals suffering from anxiety or mood disorders.
A Holistic Approach to Mental Well-being
Understanding the connection between our gut and brain opens up new possibilities for promoting mental well-being through lifestyle choices such as diet. While a ketogenic diet may offer potential benefits for individuals seeking relief from anxiety or improved mood stability, it should not be seen as a standalone solution.
Mental health is multifaceted and influenced by various factors—genetics, environment, social support, etc. A holistic approach that combines a healthy diet with exercise, stress management techniques like meditation or therapy when necessary, adequate sleep patterns, and social connections is crucial for overall mental well-being.
Recognizing how our food choices impact not only our physical health but also our emotional state empowers us to make informed decisions about nourishing both body and mind. While adhering to a ketogenic diet can potentially influence neurotransmitter production in ways that promote reduced anxiety through increased GABA levels and modulate serotonin synthesis affecting mood stability positively; it is crucial to approach mental wellness holistically.
By recognizing the intricate relationship between gut health and brain function within the gut-brain axis framework, we can appreciate how dietary choices impact our emotions and well-being. Continued research in this field will enable us to unlock further insights into how nutrition can be utilized as a valuable tool in promoting mental health.
Implications
Rebalancing the Gut Microbiome for Optimal Health
The keto diet’s impact on gut microbiota offers promising implications for those seeking to enhance their overall health and well-being. While reductions in certain bacterial species, such as Firmicutes, may initially seem concerning, the concurrent increase in beneficial bacteria like Bacteroidetes suggests a potential rebalancing effect.
This shift in microbial composition has been linked to a decrease in inflammation and improved metabolic markers. Therefore, adopting a keto diet may act as a catalyst for cultivating a thriving gut microbiome.
Potential Therapeutic Applications
Understanding the influence of the keto diet on gut health opens up exciting possibilities for novel therapeutic interventions. Emerging research suggests that the ketogenic approach has shown promising results as an adjunct therapy for various conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). By modulating the gut microbiota and reducing inflammation, the keto diet may provide new avenues for managing these challenging conditions.
Crossroads of Gut-Brain Communication
The intricate connections between the gut and brain are becoming increasingly recognized, with studies revealing that they communicate bidirectionally through various mechanisms. The impact of the keto diet on neurotransmitter production, particularly increased GABA levels associated with reduced anxiety, underscores its potential influence on mental health. By targeting both physical and emotional well-being through optimizing gut-brain axis communication, this dietary approach holds promise not only for metabolism but also for mental wellness.
Conclusion
Exploring the influence of keto diet on gut health reveals an intricate interplay between dietary choices and our body’s internal ecosystem. The changes observed in gut microbiota composition suggest that adopting a ketogenic approach can lead to favorable alterations that promote overall health. Moreover, this dietary intervention hints at new possibilities for therapeutic applications, especially in the context of gut-related disorders.
Furthermore, the keto diet’s ability to influence neurotransmitter production highlights its potential impact on mental well-being, providing a multifaceted approach to health optimization. While further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and long-term influence of keto diet on gut health, the current evidence offers promising insights.
By embracing this dietary strategy, individuals can potentially cultivate a more diverse and balanced gut microbiome while simultaneously benefiting metabolic and cognitive functions. Ultimately, by making informed choices about our diet and nurturing our gut health, we have the power to positively influence our overall well-being.
So why not embark on this journey with enthusiasm and optimism, knowing that each meal can be an opportunity to support both our physical and mental vitality? The keto diet presents an avenue ripe with potential benefits, allowing us to tap into our body’s inherent wisdom as we nourish ourselves for a healthier future.
References
Study: “Gut microbiota composition and diversity are associated with human personality traits” (2018)
This study explored the relationship between gut microbiota and personality traits in individuals following a ketogenic diet. It found that the keto diet altered the gut microbiota composition, which in turn was associated with changes in personality traits.
Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6033779/
Study: “Gut microbiota alterations in obese patients undergoing a ketogenic diet” (2019)
This study investigated the impact of a ketogenic diet on the gut microbiota of obese patients. It revealed that the keto diet led to significant changes in the gut microbiota composition, including an increase in beneficial bacteria and a decrease in potentially harmful bacteria.
Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6968736/
Study: “Impact of ketogenic diet on gut microbiota: A systematic review” (2020)
This systematic review analyzed existing studies on the ketogenic diet’s effects on gut microbiota. It highlighted the alterations in gut microbiota composition and diversity induced by the ketogenic diet and discussed their potential implications for metabolic health.
Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7160897/
Study: “The effects of a ketogenic diet on exercise metabolism and physical performance in off-road cyclists” (2020)
This study examined the effects of a ketogenic diet on exercise metabolism and gut health in off-road cyclists. It found that the keto diet altered the gut microbiota but without negative effects on exercise performance.
Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7364333/
Study: “The impact of a ketogenic diet on gut microbiota in epilepsy: A systematic review” (2021)
This systematic review explored the influence of a ketogenic diet on gut microbiota in individuals with epilepsy. It concluded that the keto diet could modulate gut microbiota composition, potentially contributing to the therapeutic effects observed in epilepsy patients.
Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8126251/
Please note that while these studies provide insights into the relationship between the ketogenic diet and gut health, it’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice or concerns about your specific situation.
Other references
Ketogenic Diets Alter Gut Microbiome in Humans, Mice | UC San Francisco (ucsf.edu)